Building Health System Resilience: A New Framework for Primary Healthcare Financing
Authors: Norah Mwase, Thulasoni Msuku, Frida Ngalesoni, and James Soki
In an era of unprecedented global challenges—from climate-related disasters to pandemics and political conflicts—health systems worldwide are under immense strain. Sustainable and strategic financing arrangements are essential for building resilient, people-centered primary health care (PHC) systems that can maintain essential functions during these crises. Yet countries face persistent financing challenges: budgeting remains largely input-based, allocations are not made directly to PHC facilities, sub-national actors often lack flexibility to reallocate funds to respond to emergency needs, funds are unpredictable and usage rates are low given rigid public financial management processes
While several tools exist to track overall health system resilience, they often lack practical guidance for assessing PHC financing. The PHC Financing Framework for Resilient Health Systems was developed by Amref Health Africa through the PROPEL Adapt project to address this gap.
What is the PHC Financing Framework?
The PHC Financing Framework is a comprehensive tool that can be used to examine and strengthen PHC financing mechanisms by identifying opportunities to improve health system resilience through enhanced predictability, service continuity, collaboration, multisectoral engagement, awareness, agility, learning, and self-regulation.
The framework was developed through a rigorous, multi-phase process, beginning with a review of 57 documents on PHC systems, health financing, and resilience. This desk research was complemented through consultations with government experts from Ghana, Ethiopia, Kenya, and Nigeria, and by adapting and leveraging lessons from existing resources such as the Health Priority Setting and Resource Allocation Benchmarking (HePRA) tool.
Several key themes emerged:
- Flexible Budgeting: Budget structures must allow flexibility to adapt to evolving health needs and priorities.
- Contingency Funds: Adequate, timely, and ring-fenced contingency funds are critical for managing emergencies.
- Direct Funding Access: PHC facilities need direct access to funds in order to operate efficiently and responsively.
- Evidence-Based Advocacy: Using strong evidence is essential for effective advocacy and engagement with political stakeholders.
- Governance and Political Economy: Governance structures and political economy significantly influence health financing strategies.
These themes, along with other findings, informed the development of the PHC Financing Framework, which is comprised of three interconnected components:
- Health Financing: resource mobilization, planning, allocation, and tracking;
- Health Financing Governance: leadership, coordination, learning, and communication; and,
- Political Economy: political dynamics that influence financing decisions.
Together, these components encompass 12 themes with 32 sub-themes, providing a nuanced assessment of how well a country’s financing arrangements are supporting resilient PHC delivery.
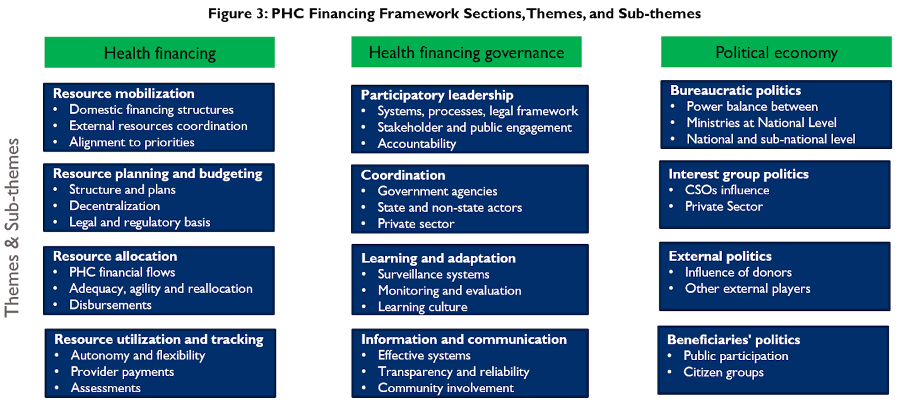
PHC Financing Framework for Resilient Health Systems sections, themes, and sub-themes.
The PHC Financing Framework is operationalized through a user-friendly benchmarking tool that employs a visual traffic light system—green indicates meeting benchmarks, yellow suggests areas for quick improvements, and red highlights critical gaps requiring sustained, immediate attention—supporting policymakers in quickly identifying strengths to maintain and weaknesses to address through concrete strategies and deliberate actions.
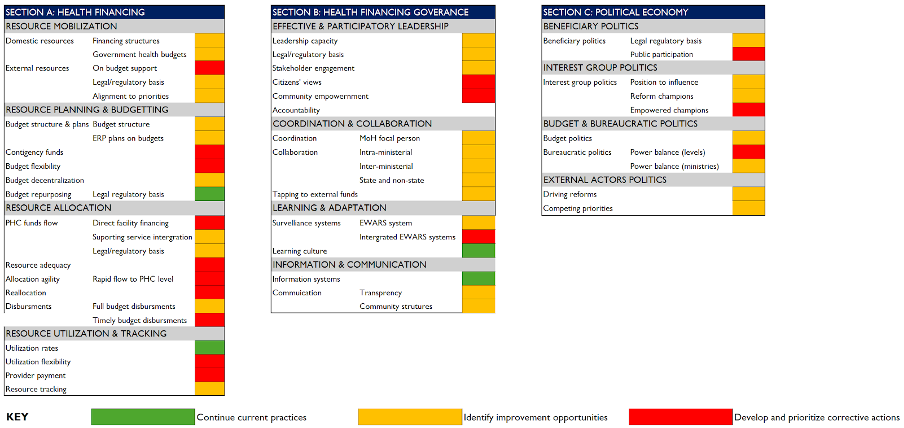
PHC Financing Framework for Resilient Health Systems benchmarks
Malawi: Piloting the Framework
The Malawi Ministry of Health helped validate the PHC Financing Framework through a participatory process that ensured the framework’s relevance, practicality, and alignment with national priorities. Malawi was an excellent candidate for this role due to its frequent exposure to climate-related hazards that strain its health system, including floods, droughts, and rising temperatures. By contributing insights on sector challenges and opportunities it is facing, the Ministry helped shape the framework’s themes and sub-themes and created an opportunity to test scalable approaches that connect climate change and public health.
“Financing is vital for building people-centred PHC, but without strong governance, resources risk being wasted and access undermined. Embedding governance in the PHC financing framework ensures accountability, equity, and real improvements in service delivery.” – Dr. Gerald Manthalu, Director of Planning and Policy Development with the Ministry of Health Malawi.
A Call for Action: Why PHC Resilience Matters Now
PHC is often the entry point for communities into the health system, and resilient PHC ensures essential services continue even in the face of global shocks. By adapting to both individual and population needs, PHC offers health security today and tomorrow.
The PHC Financing Framework represents a significant step forward in supporting more resilient primary healthcare systems—particularly those in resource-constrained or risk-affected health settings. The tool’s design allows for adaptation to different national contexts while maintaining standardized assessment approaches that enable cross-country learning.
The framework is now available as a global good for health financing actors, policymakers, and international partners to use annually in support of their efforts to track their progress in building more resilient PHC systems. The time has come to move beyond fragmented approaches to health financing and embrace systematic tools that can guide countries toward truly resilient PHC systems.
A special thanks to those who contributed to the review of the PHC Financing Framework including:
- Dr. Gerald Manthalu, Director of Planning and Policy Development with the Ministry of Health Malawi
- Thulasoni Msuku, Health Economist with the Ministry of Health Malawi
- Hester Nyasulu, Amref Health Africa Country Manager for Malawi
- Naina Ahluwalia, JLN World Bank Core Team Member. She is the Focal for the JLN Efficiency Collaborative and Health Emergency Preparedness Collaborative
- Frida Ngalesoni, Amref Health Africa Health Financing Specialist at the Health System Strengthening Directorate
- James Soki, Program Manager for the JLN
For more information on the PHC Financing Framework, reach out to Frida Ngalesoni ([email protected]) and James Soki ([email protected]).
